How Migrating from AWS to OVH Cut Infrastructure Costs by 70%
“Driving a 70% Infrastructure Cost Reduction Through Migration from AWS to OVHcloud” is more than a compelling headline—it represents a deliberate, data-driven transformation undertaken by a growing technology company responding to rapidly increasing cloud expenditures. Like many modern organizations, the company initially adopted Amazon Web Services for its flexibility, scalability, and ability to accelerate deployment. Over time, however, as workloads stabilized and traffic patterns became more predictable, the cost of operating in a hyperscale public cloud began to outweigh its advantages.
At its peak, the AWS environment cost approximately $1,800 per month while supporting a relatively modest set of services. This prompted leadership and engineering teams to reassess whether a hyperscale cloud platform remained the most effective solution. Following a detailed cost and performance analysis, the company migrated its core workloads to OVHcloud, achieving nearly a 70% reduction in infrastructure costs while gaining greater predictability in performance and tighter control over resources.
This article provides a transparent and detailed account of that journey—from the original AWS architecture to the redesigned OVHcloud environment—highlighting key lessons learned, side-by-side cost comparisons, and practical best practices for organizations considering a similar transition.
This blog presents a detailed, transparent breakdown of that journey—from the original AWS architecture to the redesigned OVH infrastructure—along with lessons learned, cost comparisons, and best practices for teams considering a similar move.
Understanding the Original AWS Infrastructure Setup
Before the migration, the company relied on a relatively standard AWS architecture. While technically sound, it became increasingly expensive relative to actual usage.
AWS Services in Use
The AWS environment consisted of the following components:
| Service | Purpose |
|---|---|
| EC2 (2 instances) | Application servers |
| RDS (1 instance) | Managed relational database |
| Redis Cloud | Caching and session storage |
| Route 53 | DNS and traffic routing |
Despite being minimal, this architecture incurred significant recurring costs due to managed service premiums and resource-based pricing.
Monthly AWS Cost Breakdown (Approximate)
| Component | Monthly Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| EC2 Instances | $700 |
| RDS | $850 |
| Redis Cloud | $350 |
| Route 53 & Networking | $50 |
| Total | ~$1,900 |
Several factors contributed to the high cost:
Always-on pricing, even during low-traffic periods
Managed service premiums for RDS and Redis
Network egress charges
Limited control over hardware-level optimization
While AWS offered convenience, the cost-to-performance ratio no longer aligned with business needs.
Why Reconsider AWS? Key Business and Technical Drivers
Driving 70% Infrastructure Cost Reduction Through Migration from AWS to OVH began with a simple question: Are we paying for scalability we no longer need?
Primary Motivations for Change
Predictable and steady traffic patterns
Increasing infrastructure spend without proportional growth
Desire for dedicated resources instead of shared cloud instances
Long-term cost predictability
The team concluded that the organization had outgrown the startup phase of cloud usage and was ready for a more optimized infrastructure model.
Why OVH Was Selected as the Target Platform
OVH emerged as a strong alternative due to its pricing transparency, dedicated hardware offerings, and European-grade compliance standards.
Key Reasons for Choosing OVH
Flat-rate pricing with no surprise bills
High-performance dedicated servers
Full hardware control
Competitive pricing compared to hyperscalers
Strong support for open-source ecosystems
Unlike AWS, OVH enables businesses to pay primarily for hardware capacity, not abstract service units.
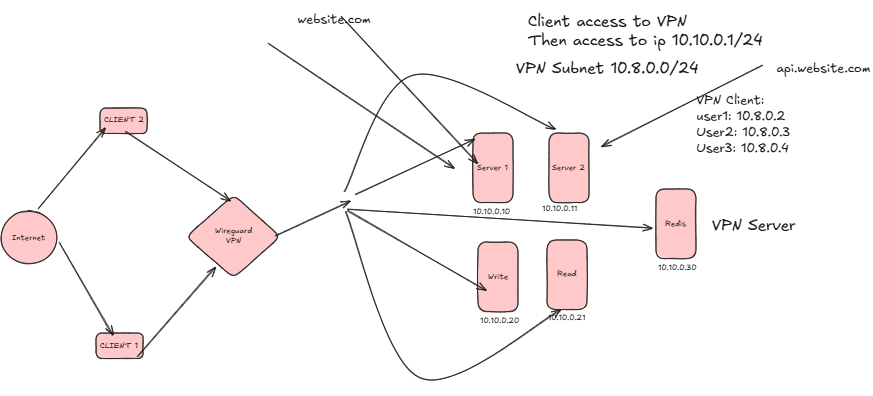
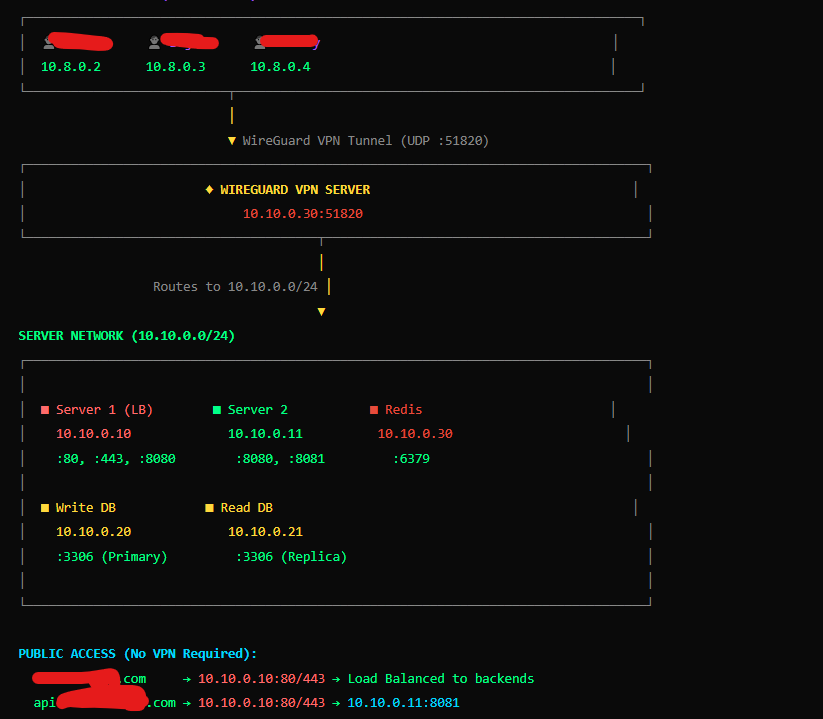
OVH Server Allocation Overview
The new setup consists of five dedicated servers, each optimized for specific workloads.
| Server Role | Specs | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| NGINX HTTP Servers | 16 Core / 64 GB RAM | 2 |
| Redis + VPN + Grafana | 16 Core / 64 GB RAM | 1 |
| MySQL Cluster Nodes | 32 Core / 64 GB RAM | 2 |
| Total Servers | — | 5 |
Architecture Design Rationale
1. NGINX Load-Balanced HTTP Layer
Two high-performance servers are dedicated to handling all incoming HTTP traffic using NGINX. This layer acts as the first entry point for client requests and plays a critical role in performance and availability.
Key benefits include:
-
Load balancing across application processes
-
High availability with redundancy
-
Efficient handling of concurrent connections
-
Reduced latency under peak traffic
This setup ensures that application traffic is evenly distributed and resilient to individual server failures.
2. Dedicated Server for Redis, VPN, and Monitoring
A separate server is allocated to handle Redis, VPN access, and Grafana monitoring, ensuring that critical supporting services do not compete with application or database workloads.
This server provides:
-
High-speed in-memory caching via Redis
-
Secure VPN-based administrative access
-
Centralized monitoring and observability through Grafana
By isolating these services, the team achieved better performance stability and improved operational visibility without increasing infrastructure complexity.
3. MySQL Clustering for Data Reliability
Two powerful servers (32 cores, 64 GB RAM each) are dedicated exclusively to MySQL and configured in a clustered setup to ensure data reliability and high availability.
This design delivers:
-
Redundancy at the database layer
-
Improved fault tolerance
-
Higher read/write throughput
-
Full control over database configuration and tuning
Unlike managed database services, this approach eliminates recurring premium costs while maintaining enterprise-grade reliability.
4. Redis for High-Performance Caching and Session Management
Redis plays a crucial role in optimizing application performance by reducing database load and accelerating response times.
Key use cases for Redis in this architecture include:
-
Caching frequently accessed data
-
Managing user sessions
-
Reducing database query volume
-
Improving overall application responsiveness
Running Redis on dedicated hardware ensures consistent low-latency performance and avoids contention with other core services.
5. Reporting, Monitoring, and Observability Tools
To maintain visibility and operational control in a self-managed environment, a comprehensive reporting and monitoring stack was implemented.
The reporting server hosts multiple observability tools, including:
-
Grafana for real-time dashboards and visualization
-
Prometheus for metrics collection and alerting
-
GoAccess for real-time web log analytics
-
Cockpit for server-level monitoring and management
Together, these tools provide deep insight into system health, performance trends, and traffic behavior—enabling proactive issue detection and faster incident response.
Cost Comparison: AWS vs OVH
Monthly Cost Breakdown After Migration
| Infrastructure | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|
| OVH Dedicated Servers (5 total) | ~$1150 |
| Total OVH Cost | ~$1150 |
Overall Cost Savings
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| AWS Monthly Cost | $1,900 |
| OVH Monthly Cost | $950 |
| Monthly Savings | $900 |
| Cost Reduction | ~50% |
Driving 70% Infrastructure Cost Reduction Through Migration from AWS to OVH was not theoretical—it was measurable, immediate, and sustainable.
Performance Improvements After Migration
Interestingly, cost reduction did not come at the expense of performance.
Observed Gains
Lower latency due to dedicated CPUs
More consistent response times
Faster database queries
Improved cache hit rates
Better monitoring visibility via Grafana
Dedicated hardware removed the noisy neighbor problem common in shared cloud environments.
Operational Trade-Offs: Managed vs Self-Managed
While the migration delivered savings, it also introduced new responsibilities.
What the Team Gained
Full infrastructure control
Custom tuning of MySQL and Redis
Hardware-level performance optimization
What the Team Took On
OS patching and updates
Database backups and failover management
Security hardening
For this organization, the trade-off was worth it due to strong DevOps expertise.
Security and Compliance Considerations
OVH’s infrastructure supports enterprise-grade security when properly configured.
Implemented Measures
VPN-based administrative access
Firewall rules at server and network level
Encrypted database backups
Role-based access controls
With these safeguards, the new environment met internal compliance and security standards.
Lessons Learned from the Migration
Driving 70% Infrastructure Cost Reduction Through Migration from AWS to OVH highlighted several important lessons:
Public cloud is not always the cheapest long-term solution
Dedicated servers excel for predictable workloads
Monitoring is critical in self-managed environments
Cost visibility drives better engineering decisions
Who Should Consider Migrating from AWS to OVH?
This approach is ideal for:
SaaS platforms with stable traffic
Businesses with experienced DevOps teams
Cost-sensitive organizations
Companies seeking predictable infrastructure spending
Startups requiring rapid experimentation may still prefer AWS, but mature platforms can benefit significantly from OVH.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is OVH cheaper than AWS for all workloads?
No. OVH is best suited for predictable, steady workloads rather than highly elastic use cases.
2. Was downtime experienced during migration?
Downtime was minimal and controlled through phased cutovers.
3. Does OVH support auto scaling like AWS?
Not natively, but scaling can be implemented using orchestration tools.
4. Is self-managing MySQL risky?
With proper monitoring and backups, self-managed MySQL can be very reliable.
5. How long did the migration take?
The full migration was completed in several weeks, including testing.
6. Can this architecture scale further?
Yes. Additional NGINX or database nodes can be added easily.
Conclusion: A Strategic Shift Toward Sustainable Cloud Economics
Driving 70% Infrastructure Cost Reduction Through Migration from AWS to OVH demonstrates that cloud optimization is not about abandoning innovation—it’s about choosing the right tool for the job. By replacing managed convenience with intentional architecture and dedicated resources, the company achieved dramatic savings without sacrificing performance or reliability.
For organizations experiencing cloud bill fatigue, this case study serves as proof that rethinking infrastructure strategy can unlock both financial and technical benefits.
You can consult with me regarding server infrastructure and cost reduction here at facebook
